Table of Contents
- – Understanding EMDR Treatment: Just How It Func...
- – The 8 Stages of EMDR Therapy
- – Accelerated Resolution Therapy: Fast-Track Tra...
- – EMDR Intensives: Concentrated Healing in Compr...
- – Dealing With Anxiety with EMDR and ART
- – Somatic Elements of Trauma-Focused Therapy
- – Selecting Between EMDR and ART for Your Needs
- – What to Anticipate From Trauma-Focused Treatment
- – Discovering Qualified EMDR and ART Specialists
Injury doesn't follow a foreseeable timeline for recovery. Traditional talk treatment aids lots of people process hard experiences, yet some memories stay stubbornly resistant to conventional approaches. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and Accelerated Resolution Therapy (ART) have actually become powerful options for individuals whose trauma signs and symptoms persist despite years of treatment. These evidence-based treatments offer pathways to relief that can really feel remarkably faster than typical techniques, occasionally generating significant changes in simply a few sessions.

Understanding EMDR Treatment: Just How It Functions
Parts workEye Motion Desensitization and Reprocessing represents a paradigm change in trauma treatment. Developed by Francine Shapiro in the late 1980s, EMDR therapy operates the concept that stressful memories become "" stuck"" in the mind's handling system, keeping their psychological charge and triggering power long after the original event. Unlike traditional treatment that depends mainly on verbal processing, EMDR uses bilateral excitement-- normally eye activities, taps, or tones-- to help with the mind's natural healing mechanisms.
The process includes recalling terrible memories while simultaneously participating in reciprocal stimulation. This double attention shows up to allow the brain to recycle stuck memories, decreasing their psychological strength and incorporating them into wider life stories. Customers usually describe the experience as enjoying a flick of their trauma that progressively loses its power, changing from a natural reliving into a farther recollection.
What makes EMDR particularly compelling is the extensive study sustaining its effectiveness. The World Health Organization, American Psychiatric Organization, and Division of Veterans Affairs all identify EMDR as an evidence-based treatment for injury and PTSD. Researches continually show that EMDR produces outcomes equivalent to or much better than standard trauma-focused cognitive behavior modification, typically in less sessions.
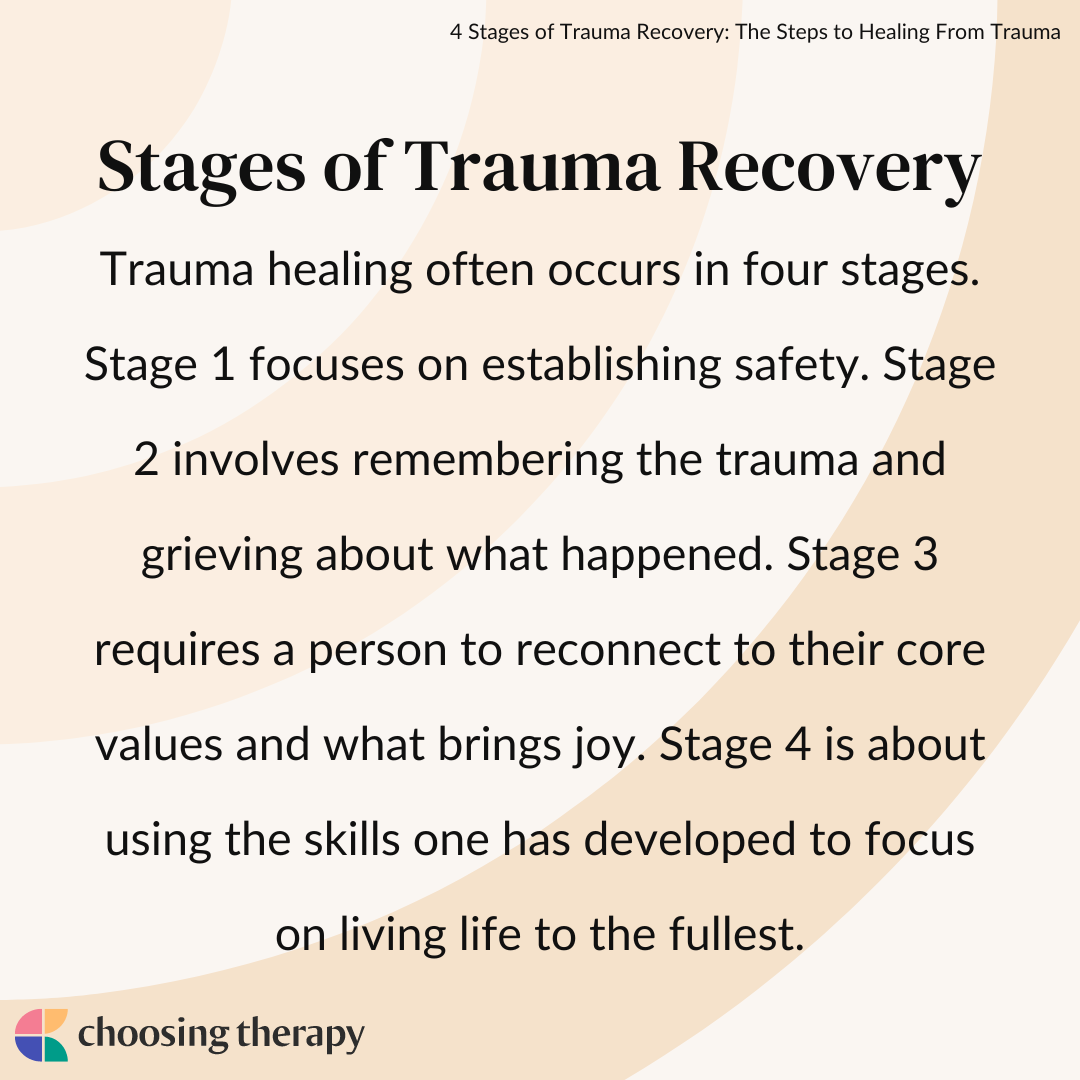
The 8 Stages of EMDR Therapy
EMDR treatment adheres to an organized eight-phase procedure that makes sure comprehensive treatment. The process begins with history-taking and treatment planning, where therapists recognize target memories and assess customer preparedness for injury handling. This preparation phase confirms important-- therapists show basing strategies and dealing abilities that customers can utilize if processing ends up being frustrating.
The evaluation phase involves identifying particular memories, unfavorable ideas connected with those memories, and wanted favorable beliefs. A memory of an auto accident could lug the negative cognition "" I'm not safe,"" which treatment intends to replace with "" I endured and I'm safe currently."" Clients rate their distress degrees and idea toughness, supplying quantifiable markers of progress throughout therapy.
Desensitization-- the heart of EMDR-- includes recalling the target memory while adhering to the specialist's relocating hand or involving with reciprocal faucets or sounds. Handling proceeds till the memory's emotional cost diminishes significantly. Installation reinforces the favorable idea, while body scan makes certain no residual physical stress stays. Closure and reevaluation phases full each session and assess development gradually.
Accelerated Resolution Therapy: Fast-Track Trauma Handling
Accelerated Resolution Therapy improves EMDR's structure while introducing distinct aspects designed to quicken healing. Created by Laney Rosenzweig in 2008, ART shares EMDR's use eye movements yet incorporates imagery rescripting techniques that enable clients to psychologically "" transform the network"" on traumatic memories. This technique typically creates remarkable cause incredibly short durations-- generally one to five sessions.
The accelerated nature of ART originates from its direct targeting of sensory memories. Instead of substantial spoken handling, ART concentrates on replacing troubling images with neutral or positive ones while keeping factual memory of occasions. A professional could bear in mind the realities of a fight experience without the intrusive nightmares and recalls that previously accompanied those memories.
ART therapy demonstrates particular performance for single-incident traumas like accidents, assaults, or clinical procedures. The protocol enables clients to maintain the material of their trauma exclusive if desired-- specialists don't require in-depth verbal summaries to assist in reliable handling. This attribute allures to people unwilling to vocally state unpleasant experiences or those worried concerning discretion in specific professional contexts.
EMDR Intensives: Concentrated Healing in Compressed Timeframes
Typical regular treatment sessions function well for lots of people, but some situations ask for even more extensive treatment. EMDR intensives condense treatment into longer, much more constant sessions-- often complete or half-day appointments over consecutive days. This layout enables deeper handling without the interruption of going back to daily life in between basic 50-minute sessions.
Intensives especially benefit individuals taking care of specific traumatic events, preparation for significant life transitions, or those that have actually plateaued in standard therapy. The concentrated style develops momentum that can appear resistance and permit processing that may take months in weekly sessions. Travel from out of state ends up being feasible when treatment presses into a week or vacation instead of needing months of normal appointments.
Resilience Currently and similar customized practices frequently structure intensives around individual demands, combining EMDR with corresponding methods like somatic therapy or mindfulness techniques. The intensive layout needs careful preparation and follow-up support to make sure clients can incorporate their processing and maintain gains after returning home.
Dealing With Anxiety with EMDR and ART
While EMDR and ART constructed their credibilities dealing with trauma and PTSD, both techniques demonstrate effectiveness for anxiety conditions also without clear traumatic beginnings. Panic attack, social anxiety, and generalized anxiety frequently have roots in earlier experiences that might not certify as capital-T injury but however created long-term patterns of worry and evasion.
EMDR targets the memories, scenarios, and sets off that fuel existing anxiousness. A person with social anxiousness may refine very early experiences of humiliation or denial that developed ideas about being evaluated or insufficient. As these memories shed their psychological fee through reciprocal excitement, contemporary anxiety signs and symptoms typically decrease dramatically.
ART's rapid handling makes it particularly appealing for individuals whose anxiousness conflicts with job, partnerships, or lifestyle. The prospect of meaningful alleviation within a handful of sessions motivates people who may otherwise delay looking for treatment. Both methods provide hope that anxiety does not call for years of administration-- it can possibly deal with via targeted reprocessing of the experiences that established anxious patterns.
Somatic Elements of Trauma-Focused Therapy
Both EMDR and ART recognize that injury lives in the body as much as the mind. Traumatic memories often materialize as physical feelings-- rigidity in the upper body, nausea, muscle stress-- that continue also when the initial danger has passed. Effective injury treatment addresses these somatic parts instead of focusing specifically on ideas and emotions.
During EMDR processing, clients track physical feelings as memories change. Tension might initially increase before launching, or brand-new feelings could emerge as processing continues. Specialists guide focus to these body experiences, enabling them to inform and progress the reprocessing work. The body scan phase particularly guarantees that no residual physical holding patterns continue to be after cognitive and emotional processing completes.
This somatic understanding confirms especially essential for complex trauma, where hypervigilance and physical reactivity ended up being embedded survival actions. Learning to track and release body-based injury reactions helps clients redeem a feeling of safety and visibility that trauma had actually taken.
Selecting Between EMDR and ART for Your Needs
Both EMDR and ART supply effective injury therapy, however certain factors could make one better for your certain circumstance. EMDR's comprehensive research base and eight-phase structure allure to individuals that value thoroughly validated techniques and value clearly specified therapy procedures. The method's flexibility enables adaptation for intricate trauma, attachment injuries, and continuous tight spots.
ART's fast outcomes make it ideal for single-incident injury, certain anxieties, or circumstances needing quick resolution. The personal privacy afforded by very little verbal disclosure advantages some clients, while others may miss the handling that originates from chatting with experiences. Some practitioners integrate both methods, utilizing ART for discrete memories and EMDR for even more complicated discussions.
What to Anticipate From Trauma-Focused Treatment
Beginning EMDR or ART needs readiness to involve with agonizing memories, even as the handling itself reduces their impact. Preliminary sessions focus on structure resources and ensuring appropriate coping abilities exist for handling potential distress. Quality trauma specialists never ever hurry into handling before establishing safety and stablizing.
The experience of bilateral stimulation varies-- some people barely observe eye motions or taps, while others find them initially unusual or disruptive. The majority of clients adapt rapidly, and the reciprocal part soon discolors right into background awareness as processing takes spotlight. Between sessions, brand-new understandings, memories, or emotions might appear as the mind proceeds incorporating product.
Progress doesn't always adhere to a linear course. Some sessions generate remarkable changes while others really feel slower or harder. Relying on the process and maintaining commitment with differing experiences permits the complete benefit of these techniques to arise. Follow-up sessions evaluate whether processing holds and resolve any staying targets or new material that surface areas.
Discovering Qualified EMDR and ART Specialists
Not all specialists offering EMDR or ART have equal training or experience. Fundamental EMDR training needs conclusion of approved programs, but added examination, progressed training, and managed practice different experienced professionals from genuinely competent ones. Look for therapists certified by EMDR International Association (EMDRIA) or that've finished extensive monitored hours beyond fundamental training.
For ART, qualification calls for specific training in the procedure and monitored practice. The treatment's family member newness contrasted to EMDR means less practitioners supply it, yet expanding study assistance continues expanding availability. Specialized practices like Strength Now commonly focus especially on trauma-informed modalities, guaranteeing personnel proficiency in these methods.
During consultations, inquire about particular training, years of exercise with the method, and sorts of injury generally treated. A specialist's comfort and confidence with the method matters significantly-- efficient EMDR and ART need versatility to adapt protocols while preserving integrity to core principles. The right match integrates technological proficiency with the relational skills that make all treatment efficient.
Table of Contents
- – Understanding EMDR Treatment: Just How It Func...
- – The 8 Stages of EMDR Therapy
- – Accelerated Resolution Therapy: Fast-Track Tra...
- – EMDR Intensives: Concentrated Healing in Compr...
- – Dealing With Anxiety with EMDR and ART
- – Somatic Elements of Trauma-Focused Therapy
- – Selecting Between EMDR and ART for Your Needs
- – What to Anticipate From Trauma-Focused Treatment
- – Discovering Qualified EMDR and ART Specialists
Latest Posts
Attention Variations and Therapeutic Intervention
Evaluating Psychoanalytic Approaches from Alternative Approaches in Chicago
Why Neuroscience Shapes Trauma Therapy
Navigation
Latest Posts
Attention Variations and Therapeutic Intervention
Evaluating Psychoanalytic Approaches from Alternative Approaches in Chicago
Why Neuroscience Shapes Trauma Therapy